Milling is one of the most widely used machining processes in modern manufacturing. In milling operations, a rotating cutting tool removes material from a workpiece to produce flat, curved, or complex surfaces. Milling machines can handle a wide variety of parts, making them essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and toolmaking. This article explains 16 common types of milling operations, how they work, and where they are applied in practice.
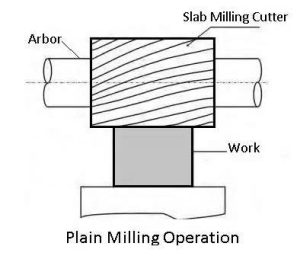
1. Plain Milling (Slab Milling)
Plain milling, also called slab milling, is one of the simplest milling operations. The milling cutter is mounted on a horizontal spindle and removes material from a flat surface. The cutting is performed along the surface of the workpiece with the cutter’s axis parallel to the surface. This operation is used for producing flat surfaces of uniform thickness. It is often applied in preparing large workpieces for further machining.
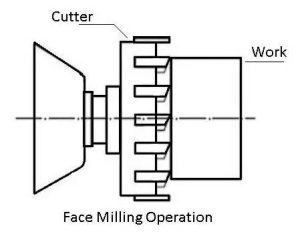
2. Face Milling
In face milling, the cutter rotates with its axis perpendicular to the surface being machined. The cutting edges are located both on the periphery and face of the tool. Face milling is ideal for creating flat surfaces with a high-quality finish. It is commonly used to machine large, flat areas such as machine housings, plates, and covers.
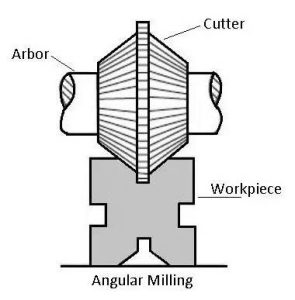
3. Angular Milling
Angular milling is used to produce flat surfaces at an angle other than 90° to the axis of the cutter. Angular cutters, such as single-angle or double-angle milling cutters, are used for this operation. This technique is often applied to machine grooves, slots, and chamfers at specific angles.
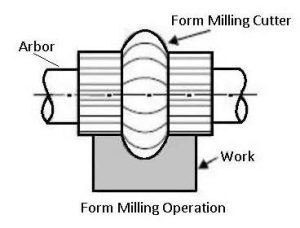
4. Form Milling
Form milling uses form cutters to create irregular contours and complex shapes such as convex, concave, or semicircular profiles. The cutter’s shape corresponds to the final contour of the part. This method is commonly used in gear manufacturing, mold making, and cutting complex surfaces in one pass.
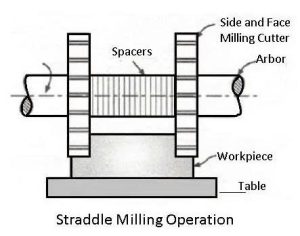
5. Straddle Milling
In straddle milling, two side cutters are mounted on the same arbor. The workpiece is passed between them to machine two parallel vertical surfaces in a single operation. It is commonly used in production when two opposite faces must be machined simultaneously, such as in keyways and slots.
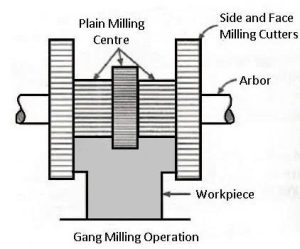
6. Gang Milling
Gang milling involves two or more cutters mounted on the arbor of a horizontal milling machine. All cutters work simultaneously, machining different surfaces of the workpiece in one pass. This technique increases productivity and is ideal for mass production.
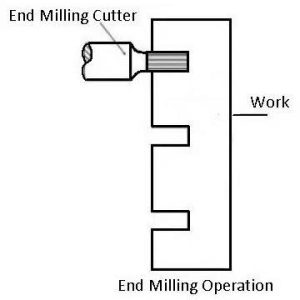
7. End Milling
End milling uses an end mill cutter with teeth on both the periphery and end face. It is one of the most versatile milling operations. End milling can produce slots, pockets, profiles, and contours. It is widely used in die and mold industries, as well as in precision machining of components.
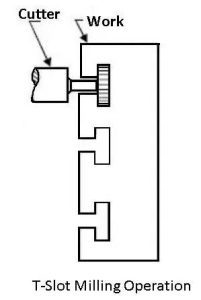
8. Slot Milling
In slot milling, the cutter removes material to produce a slot or channel in the workpiece. Slot cutters or end mills are typically used for this process. Slots can be of different shapes—rectangular, T-slots, or dovetail slots—depending on the application. This method is widely used in machine tool tables and mechanical parts.
9. Side Milling
Side milling uses a cutter with teeth on its periphery to cut along the side of the workpiece. The cutter’s axis is parallel to the surface being machined. This operation is applied to produce flat vertical surfaces, shoulders, and grooves.
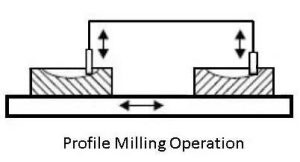
10. Profile Milling
Profile milling is the process of machining a curved or irregular outline on a workpiece. End mills are typically used for this purpose. This operation is essential in manufacturing parts with complex outer profiles, such as turbine blades and mold cavities.
11. Gang Slotting (Gang Cutting)
In gang slotting, multiple cutters are mounted to cut several slots simultaneously. Each cutter machines a specific slot in a single pass. This technique saves time in production and ensures uniform spacing between slots.
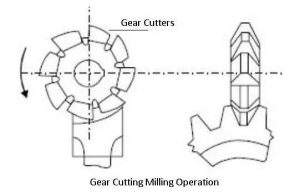
12. Gear Milling
Gear milling is used to produce gear teeth by using a form-relieved cutter or a hob. The cutter’s profile matches the gear tooth shape. This operation is widely used in gear manufacturing for automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications.
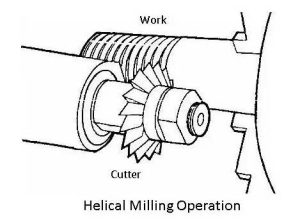
13. Helical Milling
Helical milling produces helical grooves or threads in the workpiece. The cutter is set at an angle to the axis of the workpiece. This operation is often used to create helical gears, helical flutes in drills, and threads in fasteners.
14. Cam Milling
Cam milling uses a milling machine to produce the curved profile of a cam. A form cutter or end mill shapes the workpiece into the required cam profile. This method is important in producing camshafts for engines and mechanical automation systems.
15. Thread Milling
Thread milling is the process of cutting threads using a single or multiple-point cutter. Unlike tapping, it can cut both internal and external threads with great precision. Thread milling provides better control over thread quality and allows the machining of hard materials.
16. Fly Milling (Fly Cutting)
Fly milling, also known as fly cutting, uses a single-point cutting tool attached to a fly cutter arbor. The tool sweeps across the surface, removing a thin layer of material. This process is often used for achieving a smooth, flat finish on large surfaces.
Conclusion
Milling operations are vital in modern machining. From simple plain milling to complex helical or gear milling, each operation serves a specific purpose. By understanding the 16 types of milling operations, manufacturers can choose the best technique for efficiency, precision, and productivity. Whether in toolmaking, automotive, or aerospace, milling remains one of the most adaptable and effective machining processes.